In an era marked by digital transformation, the financial sector stands on the brink of a major evolutionary step known as open banking. This concept is not merely a trend but a comprehensive shift in how financial data is handled, shared, and utilized, promising to redefine the engagement between consumers, financial institutions, and new market entrants.
The Concept of Open Banking
Open banking refers to the practice of sharing financial information electronically, securely, and only under conditions that customers approve of. This is made possible through the usage of application programming interfaces (APIs), which allow third-party developers to build applications and services around the financial institution.
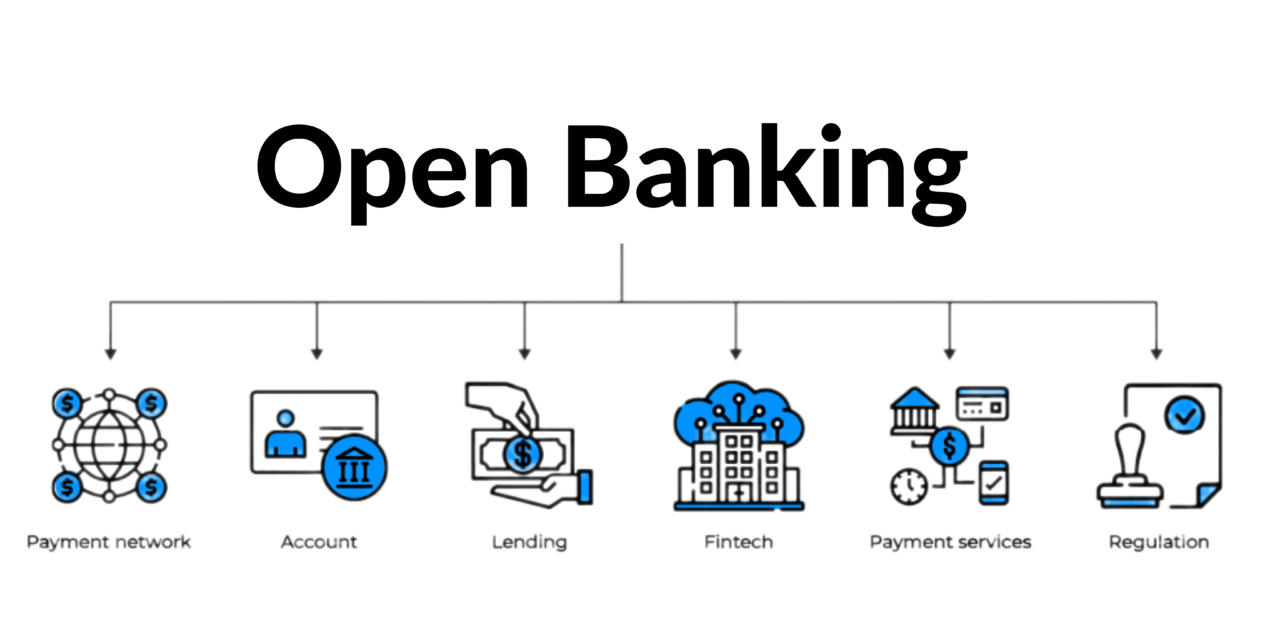
Figure 1: Understanding Open Banking Concept
Given the rising demand for personalized financial services and the global push for financial transparency, open banking has never been more relevant. It aligns with contemporary needs for technological agility in financial services and the consumer’s demand for greater control over their financial data.
Open Banking’s functionalities and benefits
This modern financial practice empowers a range of functionalities that include enhanced data sharing, direct payment initiation, and sophisticated financial management services. This innovation in banking is set to redefine the interaction between financial institutions, consumers, and new market entrants, promising a more dynamic and inclusive financial ecosystem.
1. Data Sharing:
The ability for consumers to authorize third-party providers to access their financial data is a foundational functionality of open banking. With access to rich financial data, third-party providers can offer highly personalized banking and financial services. This includes customized financial advice, tailored lending rates based on individual risk assessments, and personalized budgeting tools.
Consumers gain a clearer, comprehensive view of their financial status across different banks and financial institutions, helping them make more informed financial decisions. This transparency is a significant benefit of open banking.
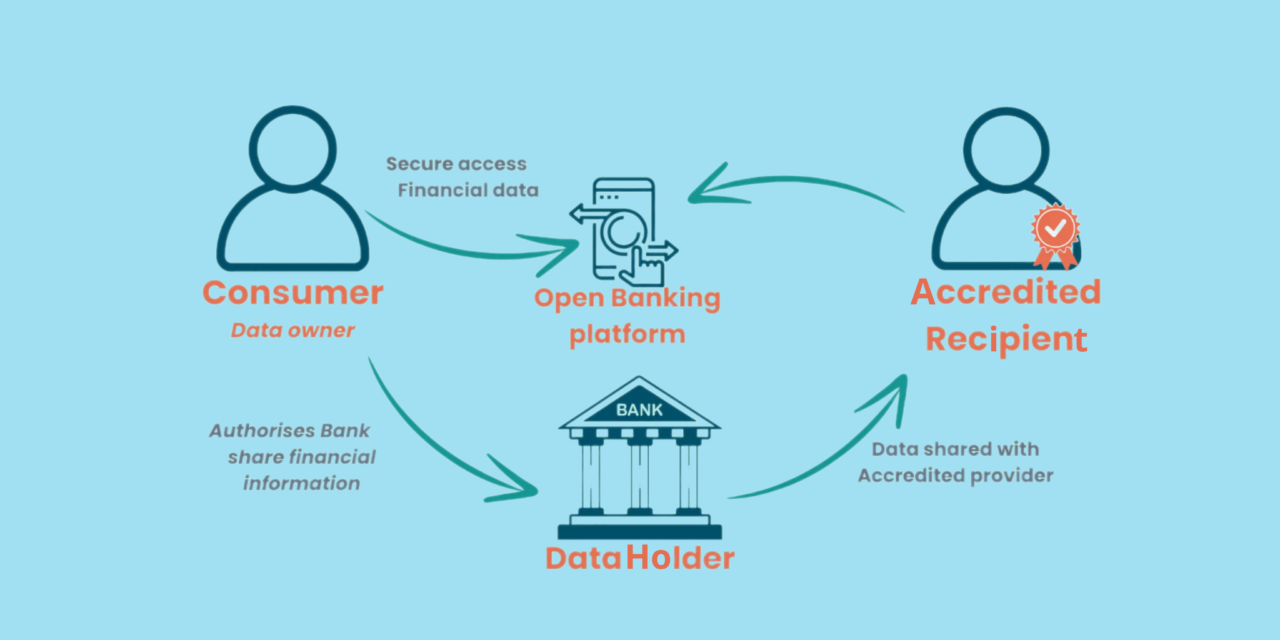
Figure 2: Data Sharing Flow
Image credit: Craggle
2. Payment Initiation:
Open banking allows third-party providers to initiate payments directly from a user’s bank account, bypassing traditional payment systems. By enabling payments that bypass credit and debit card networks, open banking can reduce transaction fees for merchants and potentially for consumers as well. Consumers enjoy a more seamless payment experience without the need to repeatedly enter payment details, particularly advantageous for recurring payments.
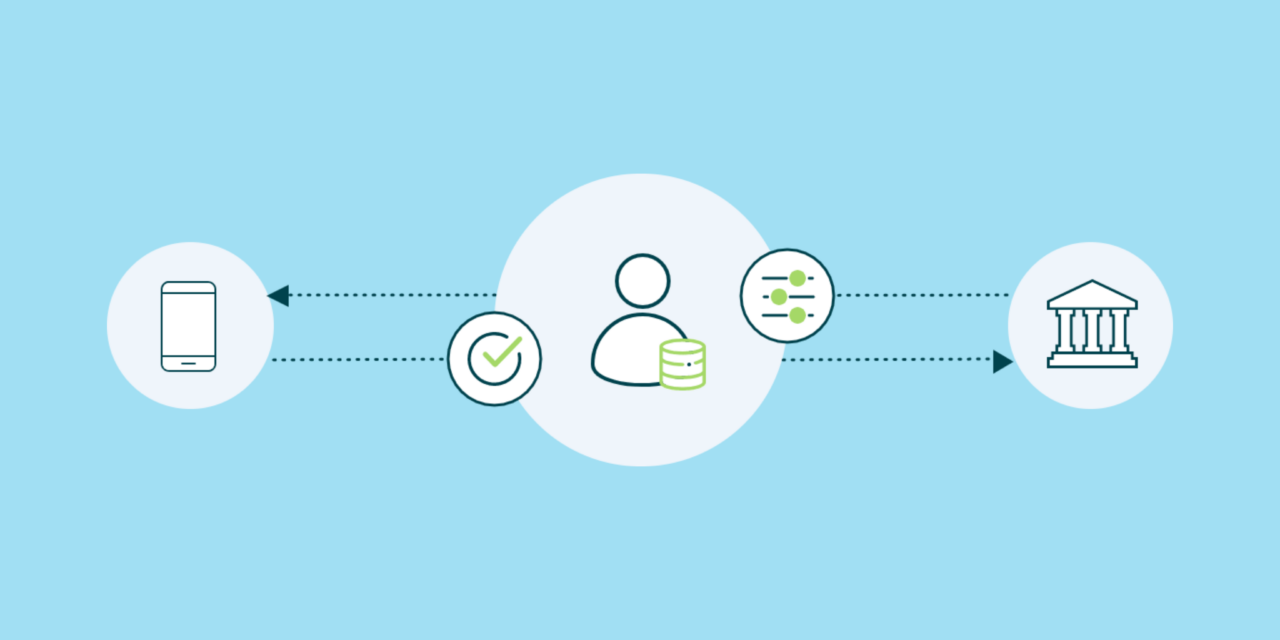
Figure 3: Payment Initiation
3. Financial Management:
Consumers can view all their financial information in one place, regardless of how many accounts they have or with which institutions. Enhanced data access allows for more sophisticated financial planning and analysis tools, offering automated insights into spending habits, investment opportunities, and more detailed budgeting assistance.
Economic Growth and Inclusion Through Open Banking
Open banking has the potential to deliver broad economic benefits by fostering a more inclusive and competitive financial landscape. The democratization of financial data through open banking enables a surge in financial innovation, allowing new entrants and fintech startups to challenge traditional banking institutions. This competition drives the development of new products and services, tailored to meet diverse consumer needs and fill market gaps.
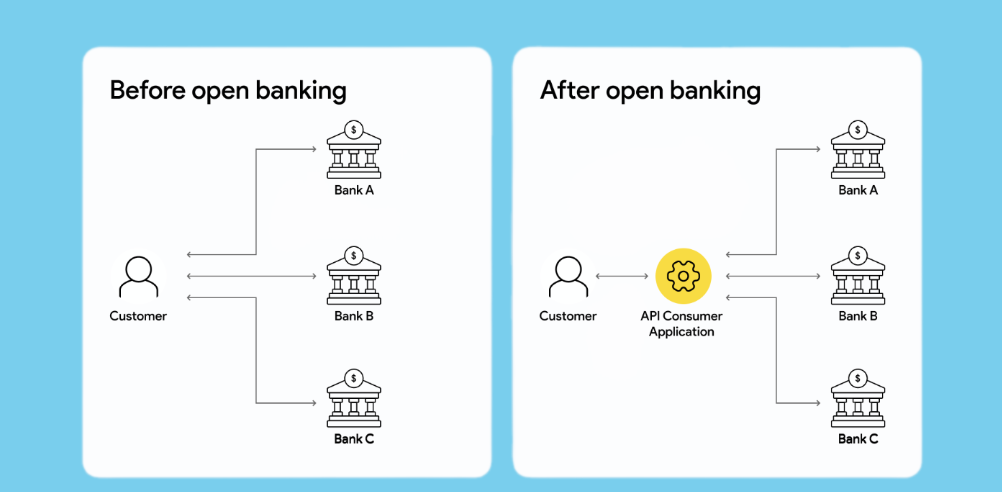
Figure 4: Economic Growth and Inclusion Through Open Banking
Moreover, open banking also significantly contributes to financial inclusion, a key economic driver. By simplifying access to financial services and creating opportunities for customized financial products, open banking reaches underserved populations, including those in rural or lower-income regions. This increased accessibility not only helps individuals manage their finances more effectively but also enables small businesses to thrive by facilitating smoother access to credit and financial resources.
Expansion of Open Banking Beyond Traditional Finance
Open banking is making waves beyond the realm of traditional financial services, transforming industries such as fintech, e-commerce, real estate, and healthcare. This evolution highlights the versatile and far-reaching impact of open banking technologies, enhancing efficiency, transparency, and customer experience across multiple sectors.
- Fintech – Personalization and Innovation: In fintech, open banking fuels innovation by providing real-time financial data access with customer consent. This enables companies to develop personalized financial solutions, such as AI-driven budgeting tools, customized investment advice, and instant loan approvals. Imagine a fintech app that analyzes your spending patterns and offers tailored investment opportunities—open banking makes this possible, creating a deeply personalized user experience.
- E-commerce: Seamless Payments and Loyalty: In e-commerce, open banking redefines the payment landscape by enabling direct bank-to-bank transactions. An online store where you can pay directly from your bank account without entering card details, combined with personalized offers based on your purchase history. This reduces reliance on traditional payment processors, cutting transaction fees and streamlining the checkout process.
- Healthcare: Efficient Billing and Payments: Healthcare providers can leverage open banking to streamline billing and payment processes. Patients can authorize direct payments from their bank accounts for medical services, reducing administrative burdens and errors.
- Broad Implications: Driving Innovation and Inclusion: The reach of open banking extends into promoting financial inclusion and driving economic growth. By democratizing access to financial services, open banking enables underserved populations to benefit from customized financial products. Small businesses and individuals gain easier access to credit and financial tools, fostering a more inclusive and dynamic economic landscape.
Challenges and Concerns with Open Banking
Open banking, while revolutionary, brings with it challenges, notably in data security and integration complexities. The openness required to share financial data via APIs increases vulnerability to data breaches and cyberattacks, demanding stringent security protocols like encryption and secure authentication. Integrating these APIs with traditional banking systems also presents technical difficulties, requiring substantial investment and upgrades to ensure interoperability across diverse platforms and systems.
Figure 5: Challenges and Concerns about Open Banking
Consumer trust remains a pivotal issue; overcoming skepticism about data privacy and security is crucial to broader adoption. Success in open banking will depend on the collective effort of all stakeholders to address these challenges effectively, paving the way for a secure and inclusive financial ecosystem.
A Real-World Case Study: Tesco Bank’s Struggles with Open Banking
Not all attempts at open banking have been successful. Tesco Bank’s early attempt at open banking is a warning to others. Despite having a large customer base and extensive resources, Tesco Bank struggled to implement open banking effectively.
The main issues faced by Tesco Bank included:
- Integration Challenges: Tesco Bank found it difficult to integrate open banking APIs with its legacy systems, leading to frequent technical issues and downtime.
- Consumer Adoption: Many Tesco Bank customers were hesitant to adopt open banking services due to concerns about data security and privacy, coupled with a lack of clear communication and education on the benefits.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating the complex regulatory landscape proved challenging, with Tesco Bank facing several compliance issues that delayed the rollout of its open banking services.
This case underscores the importance of robust technical infrastructure, consumer trust, and clear regulatory strategies in the successful implementation of open banking solutions.
Prospects and Trends in Open Banking
The economic benefits of open banking are substantial, driving innovation and competition while promoting financial inclusion. However, the path to realizing its full potential is fraught with challenges, including data security concerns and integration complexities. Addressing these challenges will require robust security measures, significant investments in technology, and efforts to build consumer trust.
Looking ahead, the integration of advanced technologies like AI and blockchain, coupled with the global expansion of open banking regulations, will further transform the financial landscape. This will create a more interconnected and standardized global financial system, enabling seamless cross-border services and fostering greater financial inclusion. As the industry adapts to these changes, the potential of open banking to reshape financial services will continue to unfold, heralding a new era of financial innovation and accessibility.
For those ready to explore and invest in embedded finance solutions, the moment is ripe. Embrace the future of finance and take the first step toward transforming your business today.
Discover how Smart81 can help you navigate this new landscape and provide cutting-edge solutions tailored to your needs. Visit our website at Smart81 to learn more and get started.



